Lift Coefficient:
Coefficient of lift CL is defined as the lifting
ability of the wing which depends on geometry of the airfoil. Coefficient of
Lift Changes with change in angle of attack and it differs for symmetric and Assymetric
airfoils.
To Know about Coefficient of lift CL we plot the
variation of lift with change in angle of attack.
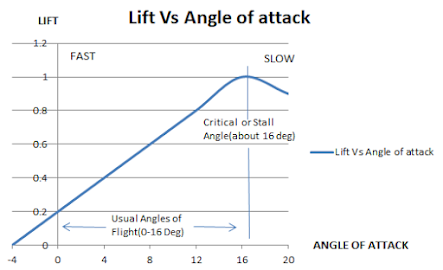
For asymmetric airfoil at 0 degree of angle of attack the lift generated is minimum and at 15-16 degrees its maximum which is called CL max. Angle of attack remains a straight line between 0 -12 Degrees. Above 12 Degrees rate of increase in lift reduces and forms a peak. The Peak formed denotes the maximum Angle Of attack CL max. At angles of attack beyond this point Coefficient of lift CL decreases which tends to reduce the lift.
Now the Airfoil is stalled and it cannot produce further lift to
maintain steady straight and levelled flight. The Angle at which CL max occurs
is called stalling angle of attack of the Airfoil.
The normal range of the Airfoil is between 0 Deg angle of
attack and stalling angle of attack.
For symmetric airfoils at 0 degrees of angle of attack there
is no lift. Each airfoils possess its own lifting Characteristics, so it’s
possible to compare Assymetrical and Symmetrical Airfoils.
Assymetrical Airfoils generate lift at low angle of attacks
and produce stall at low angle of attacks than a symmetrical Airfoil.

Nice
ReplyDeleteGood one 👍
ReplyDelete